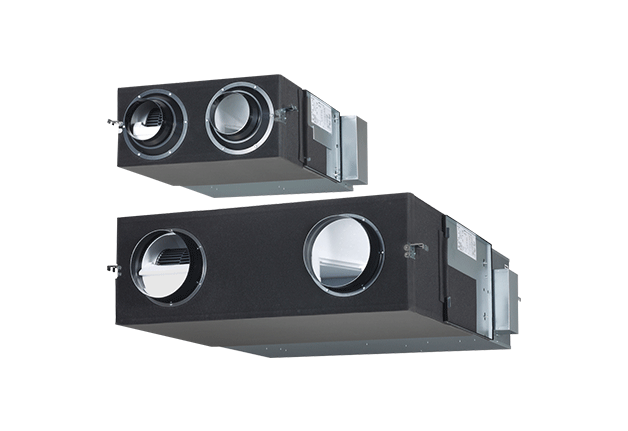
Ventilation Energy Recovery Ventilator
Features
Heat exchange ventilation and normal ventilation
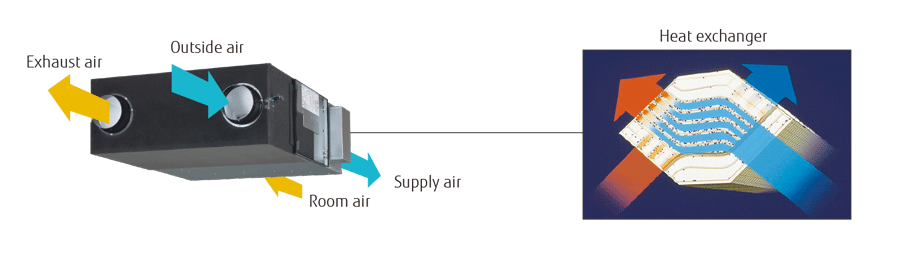
A highly efficient counterflow heat-exchanging element is incorporated.
Heat exchange ventilation
When a room is cooled or heated, the exhausted cooling or heating energy is recovered by heat exchange ventilation.
Normal ventilation
Normal ventilation is used in spring and autumn, when there is little difference between indoor and outdoor temperatures and there is no need to cool or warm the room. During summer nights, when outdoor temperature drops, the cool outdoor air is drawn indoors without heat exchange, easing the load on an air conditioner.
Greater energy efficiency
Energy efficiency and ecology
The use of a counterflow heat-exchanging element, designed to recover up to 77% of heat from the outgoing air, significantly reduces energy consumption. The air conditioning load is reduced by approximately 20%, which results in substantial savings in energy cost.
Comparison of heat-exchanging elements

Air flows in a straight line through a crossflow element. In contrast, air flows for a longer time (a longer distance) through a counterflow element to achieve more consistent heat-exchanging performance.
Greater comfort
Quiet operation
Significantly reduces the low-pressure loss and noise level.
Design flexibility
Extended range of external static pressure
The use of a powerful fan motor improves the external static pressure.
This makes it easy to install in a variety of buildings.
Easy to install and maintain
Slim design for easier installation
The use of a counterflow heat-exchanging element made it possible to design a quieter, slimmer unit.

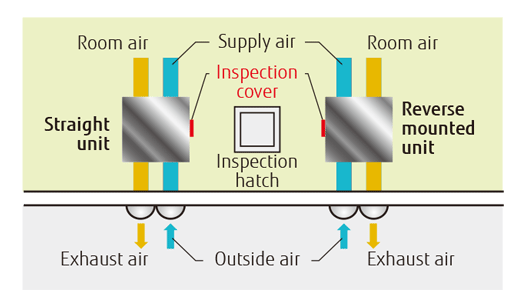
Reverse-mountable direct air supply and exhaust system
The straight-line air supply and exhaust system simplifies the duct design.
As each unit can be mounted in reverse position, only one inspection hole is needed for the two units. This makes duct work easier and more flexible.





 Europe | English
Europe | English
